Environmental Protection - AMSSNuR
Environmental protection
Protecting the environment and the population from ionizing radiation relies primarily on monitoring environmental radioactivity. Society’s growing attention to environmental issues has heightened the interest in this monitoring by all interested parties, from operators and authorities to professional associations and non-governmental organizations.
Indeed, it is important to monitor and study the fate of radioactive substances that end up in the environment, whether of natural or man-made origin (fallout from atmospheric nuclear testing, discharges from nuclear facilities, etc.).
The aim of such monitoring is to identify and quantify the substances responsible for environmental contamination and to assess their potential impact on human health and the environment (water, air, soil, fauna, flora, foodstuffs, etc.).
The aim of such monitoring is to identify and quantify the substances responsible for environmental contamination and to assess their potential impact on human health and the environment (water, air, soil, fauna, flora, foodstuffs, etc.).
To this end, facilities and activities with a radiological impact on the environment are subject to legislative and regulatory monitoring and assessment provisions designed to address this concern and ensure that radiological risk to the environment and members of the public is kept under control.

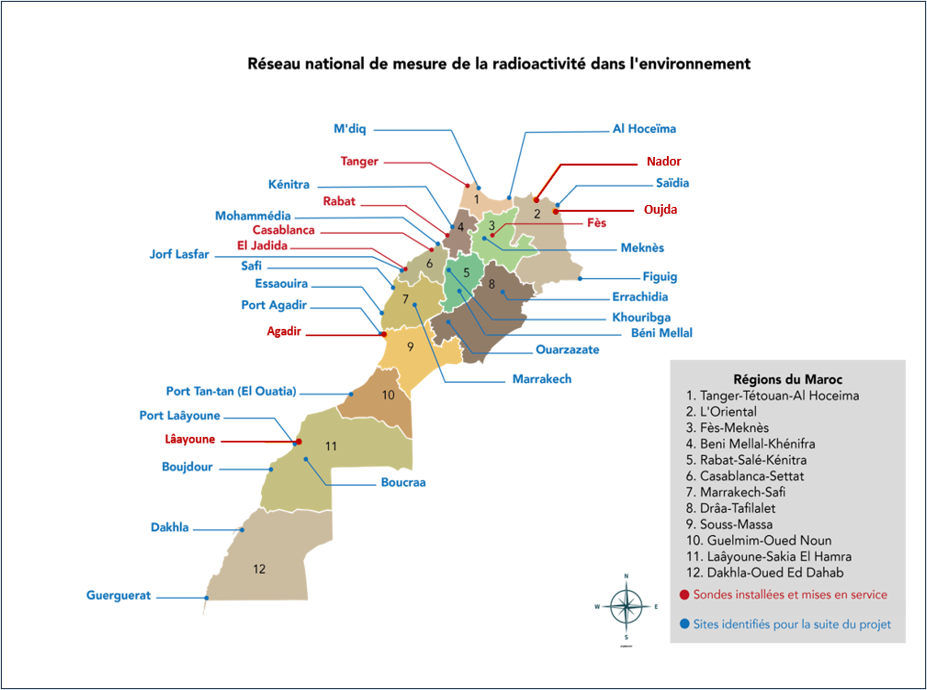
Radiological monitoring of the environment, carried out by the parties concerned, meets a number of objectives, notably the protection of the environment and populations from radiological exposure and knowledge of the radiological state of the environment. Environmental radioactivity monitoring is also aimed at the early detection of any abnormal rise in radioactivity resulting from an incident or accident.
Informing the public about the levels of radioactivity encountered in the environment also remains one of the major objectives of radiological environmental monitoring.
In addition to measuring environmental contamination, environmental protection is based on the following three components:
Managing natural sources of radiation (Radon, NORM)
Natural sources of radiation regularly release radionuclides into the environment, such as tritium, carbon-14, potassium-40, uranium, and its radioactive descendants, including radon, etc.
Radon gas, because of its danger to human health, has recently attracted particular attention from the international community.
In fact, specific regulations are required for public areas and workplaces where there is a concentration of this harmful gas.
Industrial activities that contribute to the concentration of natural radioactivity (commonly referred to as “Naturally Occurring Radioactive Material NORM”) must now be regulated. When they involve larger quantities of natural radionuclides, they require the implementation of radiation protection measures. The phosphate fertilizer manufacturing industry is an example.
Site remediation and decommissioning of nuclear and radiological activities and facilities
In order to ensure the radiation protection of the public and future users of sites housing facilities with a radiological impact on the environment, actions to rehabilitate these sites, particularly their remediation of any residual contamination, must be undertaken.
The nuclear or radiological facility can only be decommissioned if these rehabilitation actions are carried out by the operator and validated by approved service providers, and if the site where the facility is located is returned to its initial state. The decommissioning of these facilities is subject to AMSSNuR authorization.
Radiological impact assessment on the environment and the public
Prior to the authorization of any activity or facility impacting the environment, a radiological impact study must be carried out by the operator. This study is assessed by AMSSNuR, which decides on the relevance and efficiency of the actions envisaged by the operator to mitigate the radiological risk presented by his activity or facility.
