International Instruments - AMSSNuR
- International Tools
- Non-binding legal tools
- International standards
- IAEA Guidelines for Nuclear Security
Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT) (ratified in 1970).
Agreement of January 30, 1973, between the Kingdom of Morocco and the IAEA for the application of safeguards under the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (entered into force in 1975).
Additional Protocol to the Safeguards Agreement (entry into force in 2011).
Agreement on the Privileges and Immunities of the International Atomic Energy Agency (ratified in 1977).
Convention on Early Notification of Nuclear Accidents (ratified in 1993).
Convention on Assistance in the event of a Nuclear Accident or Radiological Emergency (ratified 1993).
Joint Convention on the Safety of Spent Fuel Management and on the Safety of Radioactive Waste Management (ratified 1999).
Convention on the Physical Protection of Nuclear Material (ratified in 2002).
Amendment to the Convention on the Physical Protection of Nuclear Material (entered into force in 2015).
Convention on Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage (ratified in 1999).
Protocol amending the Vienna Convention on Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage (ratified in 1999).
Convention on Supplementary Compensation for Nuclear Damage (Ratified on April 23, 1998).
Revised Supplementary Agreement on the provision of technical assistance by the International Atomic Energy Agency (signed October 2 and 6, 1992).
African Regional Cooperation Agreement for Research, Development, and Training in the Field of Nuclear Science and Technology (AFRA) – Third Extension (entered into force on April 4, 1990).
International Convention for the Suppression of Acts of Nuclear Terrorism (2005) (adopted on April 15, 2005).
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1373 (2001) (adopted by the Security Council in 2001).
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1540 (2004) (adopted by the Security Council on December 15, 2016).
Code of Conduct on the Safety and Security of Radioactive Sources (approved by the IAEA in September 2003).
Code of Conduct on the Safety of Research Reactors (adopted by the IAEA on September 24, 2004).
Additional guidance to the Code of Conduct on the Import and Export of Radioactive Sources (adopted in 2005 and revised in 2011).
Guidance on the management of Decommissioned radioactive sources (approved by the IAEA in September 2017).

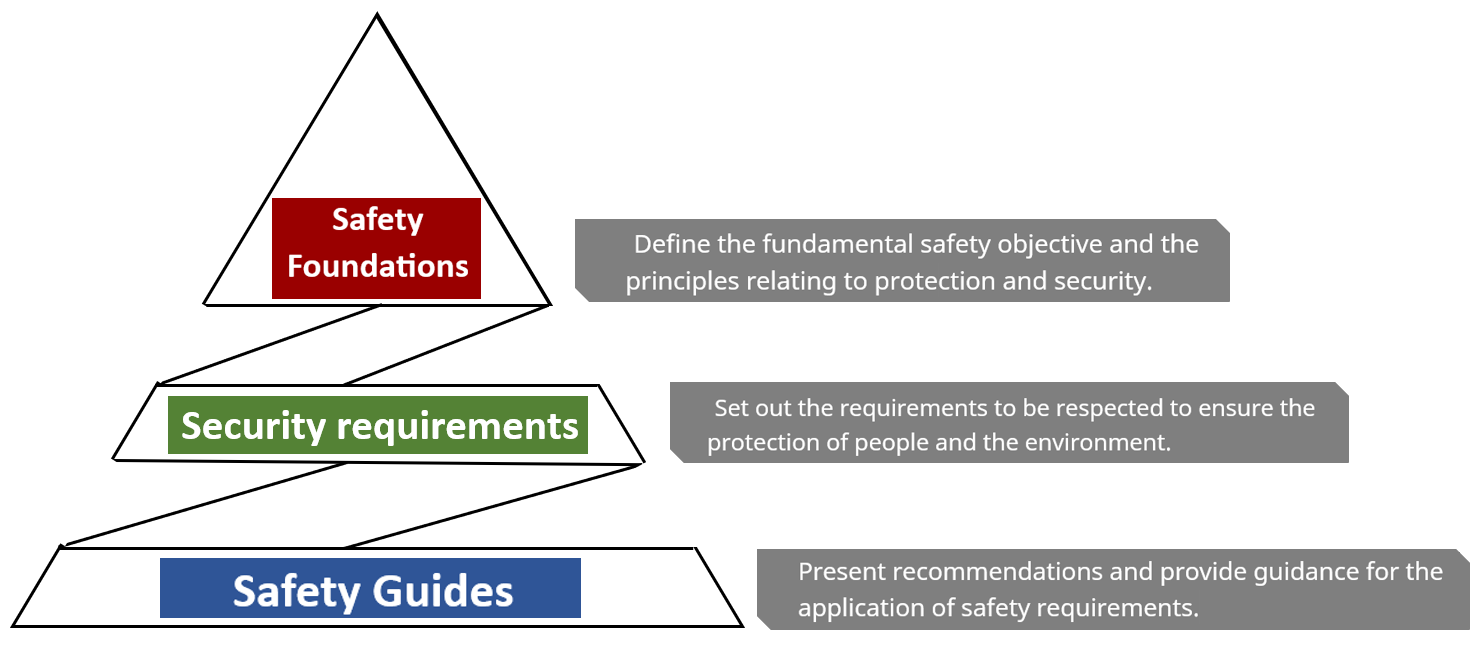
International standards, and in particular safety standards, are one of the key publications of the International Atomic Energy Agency, defining the fundamental principles, requirements, and recommendations for ensuring nuclear safety.
These standards are a global reference for the protection of people and the environment against the risks associated with the use of ionizing radiation sources and help to establish a high, harmonized level of safety throughout the world.
Safety standards cover three types of serial publications: safety basics, safety recommendations, and safety guides.
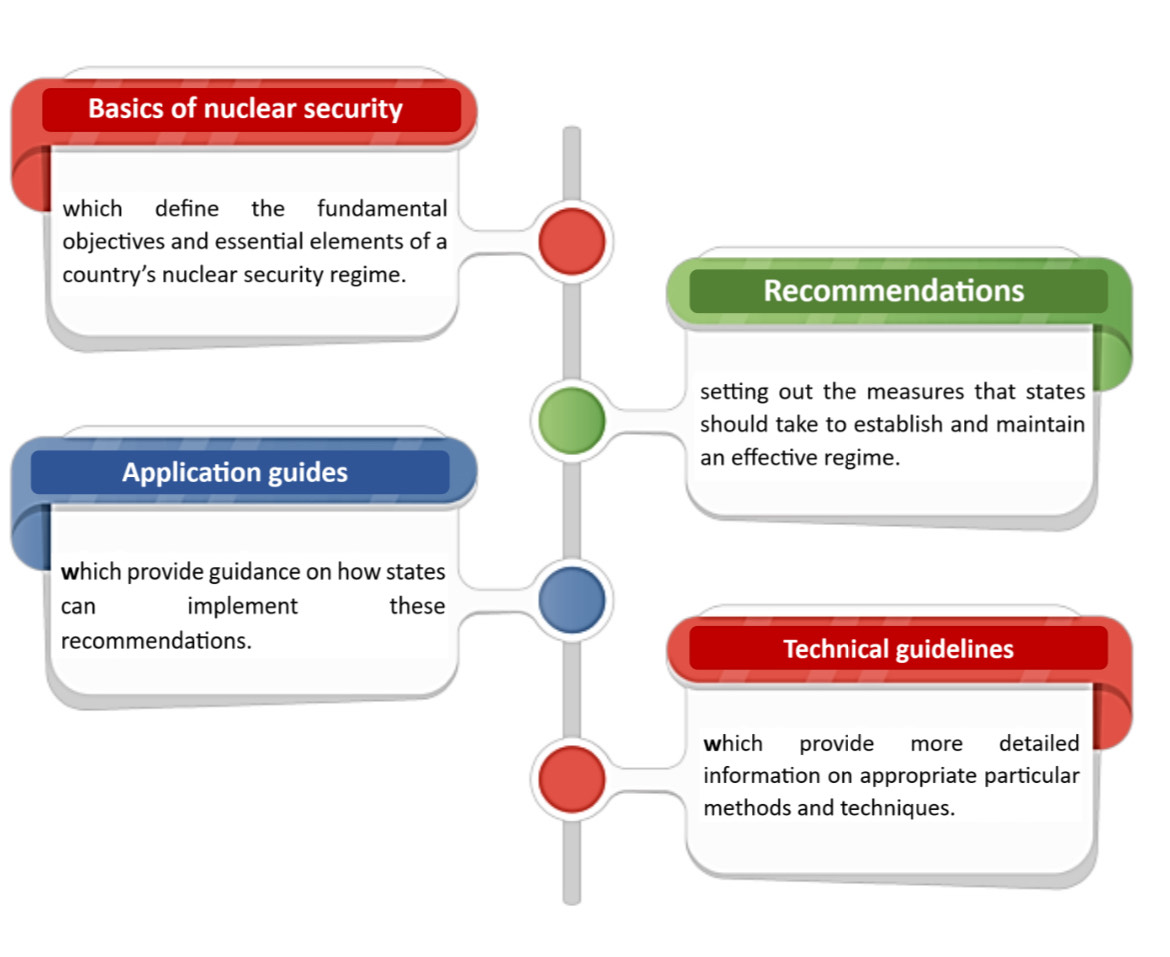
Nuclear Security Series
The IAEA’s Nuclear Security Series provides internationally agreed-upon guidance on all aspects of nuclear security to help countries meet their nuclear security responsibilities.
Nuclear security activities are intended not only to prevent or detect deliberate malicious acts involving radioactive materials or targeting facilities or activities in which these materials are used, but also to intervene when necessary.
Nuclear or radioactive materials of all types must be secured, whether in use, storage, or transport, to prevent them from being used to harm society and disrupt its proper functioning. The emergence of cyber threats and new technologies that could be used to carry out attacks or protect against them has given us an even better understanding of the need for nuclear security.